Bitcoin Cryptocurrency: Your Guide to Digital Currency and the Blockchain
Wondering what is Bitcoin? You’ve come to the right place.
Put simply, Bitcoin is the first and most popular form of cryptocurrency (crypto), which is a type of digital currency that’s decentralized thanks to its underlying technology, blockchain. This means that, unlike traditional money, which is governed by banks and central governments, no single entity has control over Bitcoin.
Today, we’re going to take a closer look at the history of Bitcoin, from its creation by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009 to the way that blockchain works, how to buy it, and what to think about when trading with it.

Bitcoin Definition and Blockchain
Understanding Bitcoin as a Peer-to-Peer Cryptocurrency

Let’s take a closer look at what is Bitcoin, starting back in 2009 when it was created by the enigmatic Satoshi Nakamoto. Nakamoto could be a pseudonym, but the truth is that we don’t really know. They’ve never been identified.
Bitcoin is known for being the first decentralized cryptocurrency, allowing peer-to-peer electronic cash transfers without the need for a central bank. Unlike traditional currencies, where new coins and notes can be minted at any time, there will only ever be a limited supply that’s capped at 21 million bitcoins.
With no central authority at the heart of it, transactions are simultaneously both more private and more transparent. Anyone can look at the blockchain to see what transfers have been made, but they can’t see who owns the wallets that the transfers are being made between.
Blockchain, Blocks and the Distributed Ledger
You can think of blockchain as being a public ledger that’s distributed among users, like a chain in which every link in the chain represents a transaction. The blockchain contains the entire history of all transactions that have been made and is distributed across users to prevent tampering and fight fraud.
With built-in cryptographic security and the fact that once a transfer has been made, it’s immutable (meaning it can’t be deleted or undone), it has everything that a cryptocurrency needs to receive widespread adoption. Meanwhile, the Bitcoin mining process rewards people for distributing the ledger and validating transactions by giving them small amounts of the cryptocurrency in return.
Bitcoin as the Digital Gold vs. Traditional Fiat Currencies

Bitcoin payments
A fiat currency is a currency like the US dollar, which is government-issued and controlled by a central bank. They’re very different in comparison to Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, because crypto is decentralized and the supply is controlled by an algorithm and not a bunch of middle-aged men in suits.
Neither fiat currency nor cryptocurrency is backed by physical commodities like gold or silver, but while fiat currency is valued based upon government decree and economic stability, cryptocurrency follows the laws of supply and demand. It’s the ultimate example of democracy in action.
Bitcoin’s Current Price and Market Value
The Price and Value of Bitcoin Today
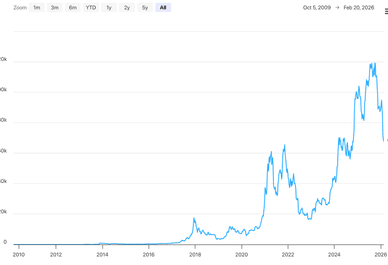
Bitcoin Price History Chart (Since 2009)
There’s no easy answer to the question of how much is Bitcoin worth, because the price is driven by supply and demand. In other words, just because it’s worth one thing today, it doesn’t mean that it’ll be worth the same amount tomorrow.
Bitcoin’s value is also partly determined by its market cap dominance, which is essentially due to the fact that it has a large share of the total crypto market and that people trust Bitcoin more than the competition. There’s also the fact that there’s a limited supply that’s capped at 21 million coins, and no more coins will ever be minted after that.
Still, the price of Bitcoin tends to vary a lot, and it’s often impacted by wider market trends, speculation, and crypto news.
Bull and Bear Markets and Consumer Sentiment
Bitcoin today tends to display a high level of interest and volatility, with institutional trends showing heightened adoption from asset managers, corporations, pension managers and other traditional financial institutions, which are starting to see its value as an investment. With that said, it’s not uncommon for the market to switch from being a bull market (with rising prices) to a bear market (with falling prices) and back again.
Meanwhile, Bitcoin-based exchange-traded funds (ETFs) have further boosted accessibility and adoption, while regulatory developments continue to affect sentiment both positively and negatively, depending upon what’s announced. The market is also impacted by the performance of traditional markets and the halving cycles, which occur every four years or so and which cut the reward for mining new Bitcoin blocks by 50%, reducing the supply of new coins entering the market.
Bitcoin vs. Altcoins: Market Share and Ecosystem
Bitcoin is known for its dominance over the market, with over half of the value of the total crypto market belonging to Bitcoin. That’s partly because it has the first-mover advantage and partly because it’s so widely accepted and well-recognised.
In fact, Bitcoin is so popular among crypto users that it’s the de facto benchmark for the crypto market, and the main health indicator that people tend to look at. There are plenty of other coins (known as altcoins), with Ethereum posing the biggest threat to Bitcoin’s dominance, but altcoins’ values tend to go up and down based on what’s happening with Bitcoin.
How to Purchase Bitcoin: Understanding Exchanges
Key Exchanges and Platforms to Know

If you’ve been wondering how to buy Bitcoin, the good news is that it’s pretty easy once you know how. The easiest way to do so is to sign up for one of the many centralized cryptocurrency exchanges, such as Coinbase, Binance, Kraken or Gemini. These platforms are designed with easy onboarding in mind, allowing people to sign up and start trading almost straight away.
There are also decentralised exchanges (DEXs), which are designed to allow users to trade between one another without any intermediaries. This gives you more control but can also require some extra technical knowledge, and so you might want to steer clear if you’re new to crypto. You can also use peer-to-peer services (which connect buyers and sellers directly) and brokerage services (which simplify the purchase process but increase fees).
Account Setup, Identity Verification and KYC Checks
When you set up an account on a cryptocurrency exchange, you’ll typically be required to go through a Know Your Customer (KYC) check. This allows exchanges to make sure that you are who you say that you are by requiring you to provide identity documents and/or proof of address for verification so that they can comply with national and international regulations.
It can take anywhere from five minutes to several days for your account to be verified, depending upon the provider. Once verified, it’s a good idea to add security features like two-factor authentication and a strong password before you attach your bank details, card details and other payment information to your account.
The Difference Between a Market Order and a Limit Order
When you spend a lot of time making trades and learning how to buy Bitcoin, you’ll start to hear terms like market orders and limit orders. The difference between these orders is that market orders buy instantly at the current price, while limit orders wait until Bitcoin is valued at a certain, preset amount before the trade goes through. There’s also spot buying (one-time purchases) and recurring purchases (which repeat and which aim to average out costs) to think about. Regardless of the type of order you place, you can expect to receive your Bitcoin in your exchange wallet immediately once the transaction goes through.
Bitcoin Wallets: A Hot Wallet vs. a Cold Wallet
Not all Bitcoin wallets are created equally. While it’s true that the goal of all wallets is to provide storage for cryptocurrency, they go about it in different ways. Hot wallets are software-based, often in the form of mobile and web apps, and remain connected to the internet. Cold wallets are stored offline and provide greater protection against hacks and attacks. Then there are custodial and non-custodial wallets, with custodial wallets being managed by third parties on their clients’ behalf.
If security is important to you, consider non-custodial cold wallets, and it should go without saying that you should never share your private keys with anyone else. Live by the mantra: “Not your keys, not your coins.”
Trading Strategies for Bitcoin
Trading vs. Investing vs. HODL

Bitcoin Wallet
Everyone under the sun has their own ideas for the best ways to approach Bitcoin trading, and many of them are in direct opposition to one another. Two of the most common investing strategies do exactly that.
The first of these is HODLing, which stands for “holding on for dear life” and relies on buying Bitcoin and keeping it in your wallet no matter what happens, with the idea that it will only increase in value over time. Then there’s active trading, in which people aim to buy low and sell high to make a profit.
Day Trading, Swing Trading and Other Techniques
Day trading is another of the most popular Bitcoin tradingstrategies, relying on tapping into those short-term price swings to buy low and sell high, often making trades multiple times in a day. Some traders even use algorithms to make trades faster than they could ever hope to do themselves, in which case they’re relying on scalping, which aims to make small profits at a rapid speed.
For traders to be successful in the long term, they need to rely on technical analysis, understanding how to read charts and knowing where to look for news, long-term patterns and other indicators of future performance. They also need to have a good grasp of risk management, which often means setting stop-losses to limit losses and reduce their overall exposure to risk.
Futures, Leverage and Other Advanced Trading Options
Now let’s take a look at spot trading and Bitcoinderivatives. Spot trading is essentially all about buying and selling Bitcoin at the current market price, while derivatives are contracts that are based upon Bitcoin’s price but without you actually needing to own any of the currency.
Finance companies often allow you to invest in derivatives without you actually needing to know anything about Bitcoin and the underlying technology. They also often offer futures, which lock in a future price, and options, which give you the choice of trading without any obligation. Leverage, meanwhile, means that traders can have larger positions with less upfront capital, but it’s also riskier because any gains or losses are magnified.
BitcoinMining and How Supply Works
How Miners Are Rewarded for Proof of Work

Bitcoin associated with blockchain technology.
Bitcoin relies on a mining progress to work, in which computers solve complicated computational puzzles to validate transactions and secure the blockchain. The idea is that the miners are able to validate the blockchain to make sure that no errors creep in, because if one mining machine makes a mistake, the others will pick it up. A transaction is only validated once the miners reach consensus.
Mining requires specialised hardware which is expensive and which consumes a lot of energy. Because of this, miners are rewarded with block rewards and transaction fees. Some miners join mining pools for steadier payouts that get shared among each participant, while others mine solo. When that happens, the rewards are a lot higher, but it’s much less likely that they’ll receive them in the first place.
Bitcoin Halving and the Effect of the 21 Million Cap
One of the most important things to know about Bitcoin is that the supply is permanently capped at 21 million bitcoins. In other words, after those 21 million bitcoins have been circulated, no more will enter the market.
Because of this, scarcity has been built into the currency as a fundamental part of how it works. Every 210,000 blocks (which happens roughly every four years), Bitcoin experiences a halving event. The block reward has fallen from 50 BTC in 2009 to 25, 12.5, 6.25, and most recently 3.125 BTC, as each halving cuts new issuance in half. This reduces the issuance of new Bitcoin by half and helps to decrease its inflation rate over time.
BitcoinRisks and Volatility
Understanding Volatility and Drawdowns
Bitcoin today is known for its relatively high volatility, because its value can often swing dramatically from low to high and back again, often over short periods of time. Since its inception, the currency has had a number of historical drawdowns of 50–80%, reflecting wider market concerns and the typical bull and bear cycles.
One of the big risks for investors is that it’s difficult to tell how long these cycles will last. During major crashes, it can be difficult for investors to sell because there just aren’t any buyers. All of this comes together to make Bitcoin investment both exciting and terrifying, and it’s only suitable for a certain type of person. If you’re in it for short-term or you try to avoid risks, it might not be for you.
Risks of Hacking and Regulation
For investors, the biggest threat is that of exchange hacks and security breaches. In other words, if those large exchanges get hacked and their security is compromised, there’s no telling what criminals might do with that high level of access. Even if your personal account isn’t compromised, a hack like this could take the entire exchange offline, which is bad news if you have a custodial wallet with them.
Other big threats include losing the private key to your wallet, which is irreversible. If you lose that, your crypto is essentially gone. There’s also uncertainty when it comes to regulation across different jurisdictions, tax implications to get to know, and some governments are taking steps to restrict cryptocurrency altogether.
Mitigation and Security Through Diversification
So what can you do to better secure yourself and your wallet? Well, that’s the million Bitcoin question.
Some of the security best practices for crypto protection include using hardware wallets and two-factor authentication, as well as ensuring that you’re using a strong password and avoiding public Wi-Fi, which is notorious for presenting security threats. Above and beyond security, you should also consider diversifying your investments beyond crypto and only risking what you can afford to lose if the worst comes to the worst.
Using Bitcoin for Payments and Wider Adoption Use Cases
Current Use Cases: Payments and the Store of Value

Payment methods compatible with Bitcoin.
One of the major use cases for Bitcoin is its use as a store of value, with it often being compared to digital gold. Fans of crypto investment say that it’s the best place to store your money to ensure that it keeps on growing in value until you need it. It’s also viewed as a hedge against inflation.
Meanwhile, its peer-to-peer payments enable people to make cross-border purchases without having to worry too much about exchange rates, and adoption among sellers is limited but growing. Most countries still don’t see it as legal tender, but that’s starting to change. In 2021, for example, El Salvador officially recognised Bitcoin as legal tender.
Scalability, Lightning Network and Other Future Developments
One of the biggest things that worries people about the future of Bitcoin is its scalability because its base layer can only cope with a limited number of transactions. That’s why people have started to look at Layer 2 solutions, such as the Lightning Network, which they hope will improve efficiency and enable faster, cheaper payments.
There’s also a concern that Bitcoin mining uses a ton of energy, and that poses a threat to the environment. A number of improvements have been made there, too. At the same time, proponents of Bitcoin are looking to find ways to encourage more mainstream businesses to accept it.
Summary and Guide for Bitcoin Beginners
If you’re looking to get started with Bitcoin today, the guide we’ve shared is designed to be perfect for beginners who are looking to understand the underlying technology and the overall marketplace.
When getting started, the best bet is to start small and to make sure that you understand what Bitcoin is, how the blockchain works, and why scarcity matters before you ever invest a cent. When it is time to invest, choose a reputable exchange and opt for a hardware wallet, especially if you’re planning on investing a significant amount.
As for trading, start by HODLing and avoid leverage initially, at least until you understand the market. Manage risk by only allocating up to 10% of your overall portfolio to cryptocurrency, and go out of your way to stay informed about the latest developments in the market. Remember that volatility is normal, and your best option is to take a long-term view.